One of the most popular listicle sites has a list of 31 science fiction stuff from movies that are now a reality, like 3d printers and surface boards. The most common trend where science fiction meets reality is based on the Internet of Things – coffee machines that make your coffee when you command, self-driven cars, automated refrigerators etc.
The Internet of Things revolves around the ability of animals, humans and machines that have sensors or identifiers, to be able to connect and transfer data over the Internet using cloud computing abilities without the need for people to interact with computers. In colloquial terms, it’s making the world around us “Smart”. For e.g. harnesses the carbon-sinking capabilities of plants to create a city-wide network of electronically-assisted plants that act as energy providers or e-Tag systems, which detect when a car enters a toll-way, takes a picture of the number plate, and automatically takes the payment from the credit card registered against that vehicle.
The IoT technology has been in use since the 1980’s, but has gained prominence and become commercially viable only lately. How has the IoT been able to make these giant strides in recent times? The IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) protocol allows for every device that is connected to the internet currently (and in the future) to be assigned an identity and location. Additionally we now have, cheaper broadband connectivity across the world with low-cost wifi devices/sensors. Therefore the ability to create this mega connection of devices over the internet makes Internet of Things a reality. As per Gartner, by 2020 there will be over 26 billion connected devices!
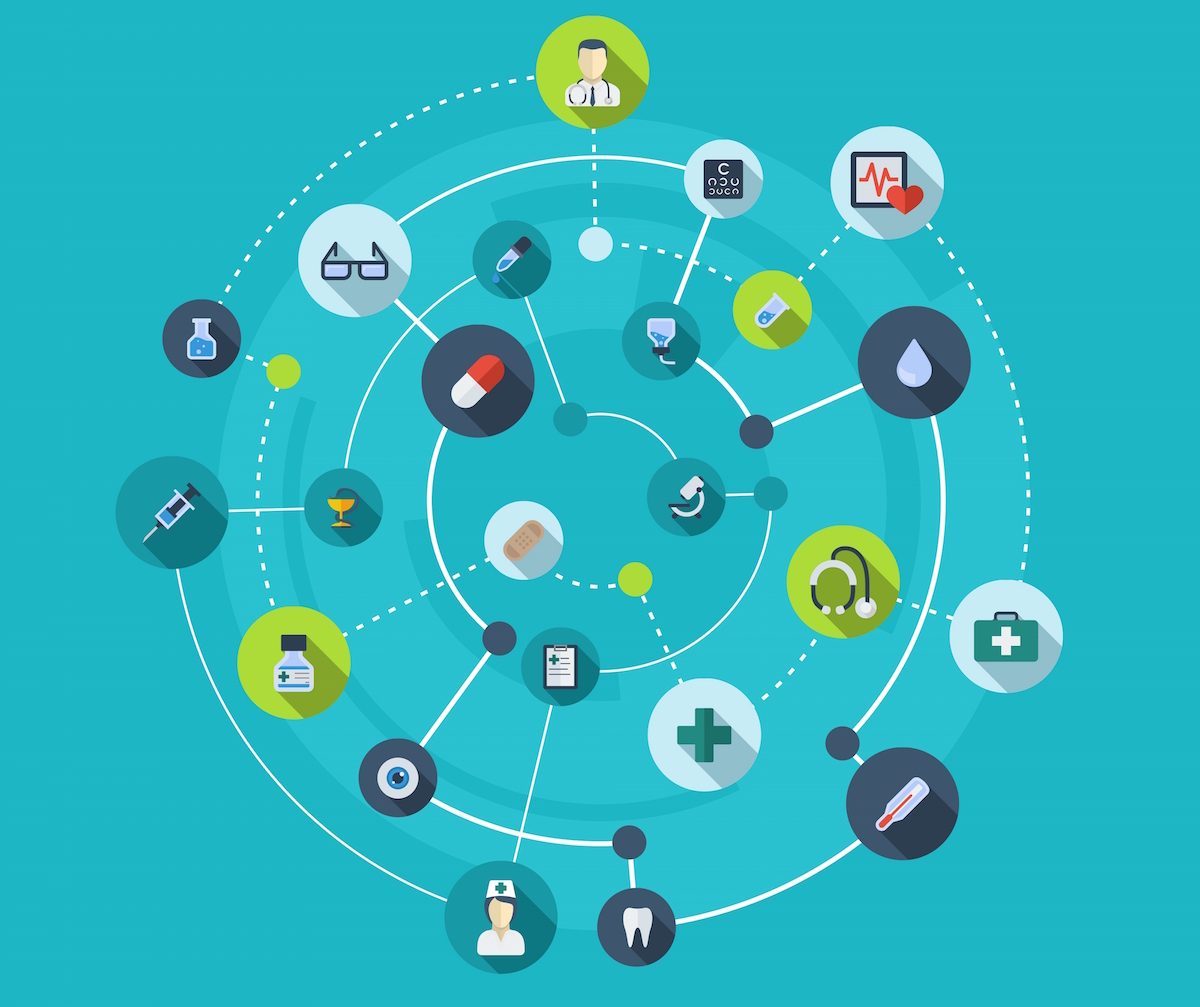
More fascinating than machine to machine utility communication, is this communication ability being used to help humans in medical aid. It has become increasingly possible to remotely monitor a patient’s health with the use of network of sensors, actuators and other devices- commonly referred to as the Internet of Things for Medical Devices (IoT-MD).
There have been quite a lot of inventions in the IoT-MD space. Wireless monitoring devices, chip placements are already a reality. There are sensor systems that can remotely read a patient’s biometrics (ECG, heart rate, respiration rate and activity Level) and send information on the health of a patient to the medical team. Imagine the convenience of this device for chronic patients who are on long term treatments. Patients have the option of staying at home and continue being monitored by doctors. Since the patient’s health is being tracked regularly, there are lesser chances of developing complications or missing medications as per routine. Additionally, as this data is available real time to medical- practitioners, chances of quick and life-saving medicine in case of an emergency is a big possibility. There are similar such devices for Senior Citizens as well, which tracks the movements and vital signs of the elderly and immediately calls the primary care-giver in case of a fall or a medical emergency.
As with everything that’s good, there needs to be some precautions before the IoT-MD are extensively used. Privacy of data over the net, chances of hacking which risks the patient’s life or devices getting corrupt causing complacency in critical care- are huge risk factors. But since the medical device segment is currently the fore-runner in the IoT scheme of things, there are already non-profit communities being formed across care-givers and medical device manufacturers in setting guidelines and standardizing devices.
We’ve only touched the tip of the iceberg. There are even more audacious ideas on Internet of Things that we are yet to see.